My best passive income strategies as a side hustle.

Staking
All cryptocurrencies have a consensus mechanism which means they have a system that verifies transactions on their ledger. Those who verify transactions are paid for their efforts in crypto.
The thing about verifying transactions is you can’t make it easy to do otherwise, bad actors can come in and attack the system.
So a good way to make it difficult to verify transactions is by requiring resources to do the verification.
This can be done by mining a cryptocurrency as bitcoin does, which needs a lot of electricity and powerful computers to verify transactions or staking your cryptocurrency.
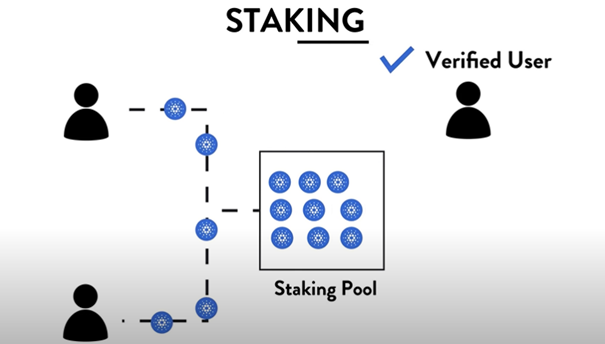
Staking allows you to verify transactions by essentially locking up or staking that currency with a validator.
The model says if you have money in the system, you’re unlikely to be a bad actor, so you can be paid staking rewards for locking up your currency and helping to facilitate the system.
The rewards are paid in proportion to how much of that crypto you hold. So if you hold 100 coins, you’ll receive ten times more staking rewards than someone who holds ten coins.
Staking rewards are typically around four to ten percent annually, but some reach as high as 100% or more. Usually, on the higher end, those are temporary rewards.
How do you stake your crypto?
Unfortunately, each crypto is slightly different. But the most user-friendly way is by going through an exchange like exodus or Binance who offers fairly good staking rewards.
Otherwise, you can stick directly from your crypto wallet to what’s called a stake pool. This generally gets you the highest possible rewards. Staking is a great option if you plan on holding a crypto long-term.
Yield Farming
Yield farming takes a bit more effort and a deeper understanding of cryptocurrencies and the risks involved.
Here you’re doing more than just putting your held coins in a stake pool to help facilitate transactions. Instead, you’re allowing your coins to be used to facilitate transactions in a decentralized exchange.
Something like Uniswap or Pancakeswap. This is called providing liquidity in a liquidity pool. So, a decentralized exchange uses your coins to let other users borrow or trade cryptos through swaps.
Swaps are swapping one coin for another, so swapping like ethereum for chainlink.
İ like to think of providing liquidity as a small business. Because you lock up your crypto in these liquidity pools, and you’re paid a percentage of all the transaction fees that that pool earns.

So if you’re providing 50 percent of the liquidity in a pool, meaning 50 percent of the currency in that pool is your currency, you get paid 50 percent of the rewards.
This means 50 percent of the fees generated you receive, which can be a lot of money.
There’s another layer to this comparison, and that’s called Liquidity Mining. With liquidity mining, you’re still allowing your coins to be used in a liquidity pool, and you’re still earning a portion of the transaction fees.
But on top of this, you also receive additional tokens, which you can trade on exchanges for additional cash. So let’s do an example. First, you provide liquidity for an ethereum link swap.
Meaning you hold both of those cryptos, and you’re locking them up with the liquidity pool. With regular liquidity providing, you get paid your transaction fee rewards in ethereum.
With liquidity mining, you get your transaction fee rewards and additional tokens from the exchange. Let’s call it token x. This means you can make even more money.
So a real-world example here is using a protocol like compound finance. You’re rewarded with comp governance tokens when you provide liquidity through their platform.
So like other governance tokens, Comp also allows users who hold that token to vote on changes within the ecosystem. You can still sell those tokens for cash, so this can be additional income from providing liquidity.
Top Strategies
The most often used strategy for yield farming involves using an Automated Market Maker or an amm. With an AMM, you’re required to invest in a trading payer.
This is the swap that I mentioned earlier, like ethereum and chainlink. Whichever two cryptocurrencies that you hold that you could help facilitate those transactions.
This is commonly a stable coin through like Usdt, or Dia paired with a slightly more volatile asset like ethereum.
By doing so, you’re providing liquidity to the amm. And you’re doing that, so users who would like to trade either one of those two assets can do so at a fairly stable price.
The reward you get is again a cut of the trading fees in proportion to how much liquidity you’re providing. The most popular places to do this are Uniswap Pancakeswap Sushiswap and 1inch.
Shortly we’ll have even more options once the Cardano ecosystem has their dexes up and running. A side note here is that AMMs allow you to deposit just one kind of crypto asset instead of the pair.
However, those are rarer. But this does put you at less risk of impermanent loss.
Some high-risk-tolerance investors take this several steps further to earn even more money. What they do is they lend and borrow from different dapps to receive the highest amount of rewards possible.
This is not something that I recommend. So basically, people will both lock up their tokens and borrow out tokens simultaneously to increase exposure and then use those tokens that they’re borrowing to provide liquidity elsewhere.
It’s like leveraged liquidity, and of course, it can get extremely risky extremely fast. Again not recommended if you’re new to this. Stick to basic liquidity providing.
The way I like to think of providing liquidity is how I like to think of staking. İf you plan on holding a project long-term, this will earn you extra income if you do your research first.
How Much Can You Earn By Providing Liquidity?
Luckily some tools can help you calculate the returns before you ever even start. For example, here, we can see that on Uniswap, if you’d provided one thousand dollars in an ethereum usdt pool, you could get a 56% return given current rates.
This is quite high returns, and of course, that is subject to volatility and other risks.
A common strategy for success when providing liquidity is only joining pools with a lot of trading volüme.
So popular coins and this is because you need trades to happen within a pool to make money. So if you’re providing liquidity for two rare coins, you’re not going to make a whole lot of money.
Risks
The first risk is a Rug Pull. When you’re buying new crypto tokens for a project that hasn’t launched officially, you run the risk that that team will take that money and run without ever completing the project.
And this also applies to defi projects where a new liquidity pool might promise you returns in the thousand or even million percent range. But then it gets shut down before you see any returns on your investment.
The scammers, of course, run away with deposited funds. This can be avoided by just sticking with popular apps and doing your research beforehand.
The second risk is Bad Market Mechanics. And this happened to Mark Cuban just a couple of months ago. He was providing liquidity for a crypto project that included crypto called Titan and Iron.
Iron was an algorithmic stable coin tied in price to the other crypto within the pool titan.
And then there was some selling pressure on titan, and this caused both the cryptos to spiral down to nearly zero almost instantly, and everyone lost all their money, including Mark Cuban.
This happened because the stable coin was simply poorly designed. But again, a situation like this is avoidable. This swap was advertising two to four million percent annual returns. So greediness gets you in trouble even if you’re a billionaire.
The last risk to consider is Impermanent Loss. This occurs when you’ve deposited two assets into a double-sided liquidity pool where it’s required that you deposit the same amount of two different tokens.

In most cases, it’s necessary to do this because many exchanges need you to have a proportional amount of both tokens for users to borrow against the pair.
So what happens is as the price of your two cryptos change, the proportion of each coin you hold changes automatically in the liquidity pool. And this happens to keep that ratio at 50 50 for each crypto.

This can be an issue if one of the tokens you deposit skyrockets in price because your position of the skyrocketing coin will begin to sell off to keep that proportion at 50 50.
Here’s where the problem comes in. İf a crypto in your pair, let’s say, doubles in price. You would have made more money by just holding that coin instead of using it to provide liquidity.
Impermanent loss is like opportunity cost of providing liquidity opportunity costs that you may miss out on monster gains. But this only happens if one coin takes off and the other doesn’t. Again because of that proportion balance.
I don’t want to worry you too much because there are methods to limit this issue, and it’s much less an issue than a couple of years ago.
On Uniswap, for example, you can choose the trading range, and if prices go beyond that range, so if that crypto doubles, the pair will stop rebalancing, meaning you won’t lose all of that upside.
Final words
So, in summary, providing liquidity can be a great way to earn a bit more money on the crypto that you plan to hold long term.
Furthermore, this is generally a stable way to earn more money so long as you aren’t holding super high-risk projects and don’t let greed get the best of you.
